Supports Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) - The purpose of spanning tree
1. To prevent loop
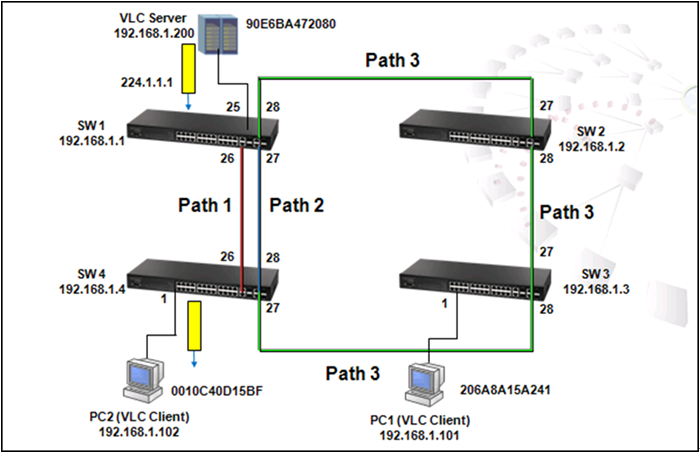
As shown in the figure above, there are 3 traffic paths from VLC server to PC2:
Path 1(red): from SW1 port 26 to SW4 port 26;
Path 2(blue): from SW1 port 27 to SW4 port 28;
Path 3(green): from SW1 port 28 to SW2 port 27, from SW2 port 28 to SW3 port 27, from SW3 port 28 to SW4 port 27 then to SW4 port 1.
Therefore, there are two loops in the topology:
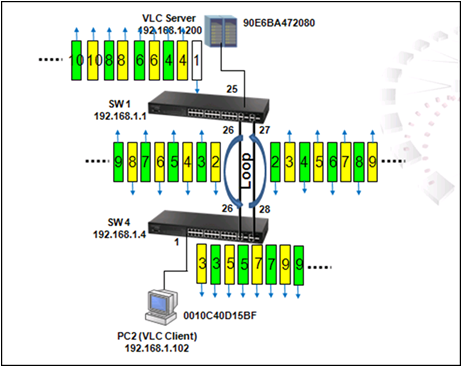
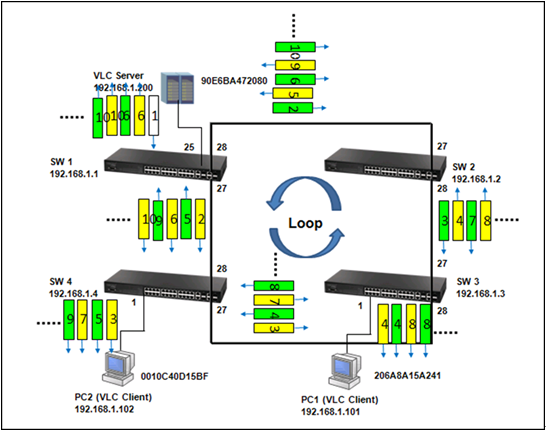
As shown in the figures above, when the switch receives a broadcast, multicast or unknown unicast packet from VCL Server, packet will flood to port 26(packet 2 yellow) and 27 (packet 2 green). When SW4 receives the packet from port 26, the packet will flood to port 1 (packet 3 yellow) and port 28 (packet 3 yellow). When SW4 receives the packet from port 28, the packet will flood to port 1(packet 3 green) and port 26 (packet 3 green). In this way, packets will occupy every port that connected to switch and it results in a failure to serving normal packets and sometimes a waste of CPU utilization.
Spanning Tree Protocol is a mechanism that automatically detects loops in the network and blocks the redundant paths to keep only one path for two nodes in the network. Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an enhancement of STP and provides faster spanning tree convergence. RSTP uses path cost, bridge ID and port priority/port ID of BPDU to prioritize the paths and then to establish a spanning tree.
2. To Provide Redundant path
Sometimes users create a loop intentionally in order to build up a redundant path in case the path is failed to link. Traffic dynamically switches to the redundant path and maintain network operation when the default path is failed to link.
When the link between SW1 port 26 and SW4 port 26 is down, SW1 port 27 which is in blocking state (Alternate Role) automatically forwards. Therefore, traffic from VLC server switches to the link between SW1 port 27 and SW4 port 28.
Use command "show log ram" to see the change log as below.
SW_1#show log ram [3] 08:59:45 2011-12-08 'STA topology change happened on Eth 1/27.' level : 6, module : 5, function : 1, and event no. : 1 [2] 08:59:45 2011-12-08 'STP port state: MSTID 0, Eth 1/27 becomes forwarding.' level : 6, module : 5, function : 1, and event no. : 1 [1] 08:59:45 2011-12-08 'STP port state: MSTID 0, Eth 1/26 becomes non-forwarding.' level : 6, module : 5, function : 1, and event no. : 1 [0] 08:59:45 2011-12-08 'Unit 1, Port 26 link-down notification.' level : 6, module : 5, function : 1, and event no. : 1
SW_4-0#show log ram [2] 08:28:56 2011-12-08 'STA topology change happened on Eth 1/27.' level : 6, module : 5, function : 1, and event no. : 1 [1] 08:28:54 2011-12-08 'STP port state: MSTID 0, Eth 1/26 becomes non-forwarding.' level : 6, module : 5, function : 1, and event no. : 1 [0] 08:28:54 2011-12-08 'Unit 1, Port 26 link-down notification.' level : 6, module : 5, function : 1, and event no. : 1
Prev Page What BGP log messages are supported on the AS5710-54X-EC ?
Next Page Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) - How do trunk ports behave in RSTP ?
